POWER
Rate of doing work is called power.
-
The unit of electric power is watt.
-
One watt of power is equals the work done in one second by one volt of potential difference in moving one coulomb of charge.
-
We know that one coulomb per second is an ampere. Therefore power in watts equals the product of volt times amperes.
-
Power in watts = volts x amperes
-
P = V X I
-
Dimensionally, the right side of this equation is the product of joules per coulomb and coulombs per second, which produces the expected dimension of joule per second or watt.
-
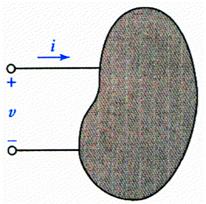
The sketch shows that if one terminal of the element is v volts positive with respect to the other terminal, and of current i is entering the element through the terminal then the power is absorbed by the element.
-
It is also correct to say that a power p =vi is being delivered to the element.
PASSIVE SIGN CONVENTIONS
-
If the current arrow is directed into the + marked terminal of an element, then p=vi yields the absorbed power.
-
A negative value indicates the power is actually being generated by the element, it might have been better to define a current flowing out of the + terminal.
Example
Q. A simple circuit is formed using a12V lead-acid battery and an automobile headlight. If the battery delivers a total energy of 460.8watt-hours over an 8 hours discharge period.
(a) How much power is delivered to the headlight?
(b) What is the current flowing through the bulb (assume the battery voltage remains constant while discharging)
Solution:
The battery delivers energy of 460.8 W-hr over a period of 8 hrs.
(a) The power delivered to the headlight is therefore (460.8 W-hrs)
(b) The current through the headlight is equal to the power it absorbs from the battery divided by the Voltage, at which the power is supplied,
OR I = (57.6 W)/(12V) = 4.8 A
Previous
TOC
Next