Symmetry:-
A very important concept. Symmetry is at the heart of
many mathematical arguments concerning the structure of the
universe, and certainly symmetry plays an important role in applied
mathematics and engineering fields. Here is what it is.
As
illustrated in Figure the points

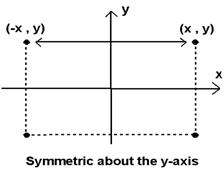
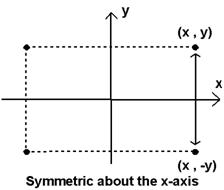
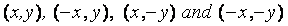
form the corners of a rectangle
For obvious reasons, the points (x,y) and (x,-y)
are said to be
symmetric about
the x-axis
and the points ( x, y) and (
-x, y) are symmetric about the y-axis
and
the points (x, y)
and ( -x, -y)
symmetric about the
SYMMETRY
AS A TOOL FOR GRAPHING
By taking advantage
of symmetries when they exist, the work required to obtain a
graph can be reduced considerably. Example#9
Sketch the graph of the equation

Solution:-
The graph is symmetric about the y-axis since
substituting
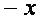
for x yields

which simplifies
to the original equation
As a consequence of this symmetry, we need only
calculate points on the graph that lies in the
right half of the xy-plane ( x  0).
0).
 0).
0).
The corresponding points in the left
half of the xy-plane ( x  0)
0)
 0)
0)
can be obtained with no
additional computation by using
the symmetry. So
put only positive x-values in
given equation and evaluate
corresponding y-values.
Since graph is symmetric
about y-axis, we will just put
negative signs with the x-values
taken before and take the same
y-values as evaluated before for
positive x-values.

Example#10
Sketch the graph of the equation

Solution:-
If we solve 
for y in
terms of x, we obtain two solutions,


The graph of

is the portion
of the curve
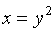
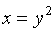
that lies above or touches the
x-axis
(since 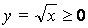 ),
),

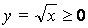 ),
),
and the graph
of
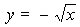
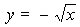
is the portion
that lies below
or touches the
x-axis (since


However, the
curve

is
symmetric
about
the
x-axis
because
substituting
-y
for
y
yields


which is equivalent to the original equation.
Thus, we need only graph
and then reflect it about the x-axis to complete the graph


is the graph of the function.

is the required graph of the function.
Previous
TOC